
You can load a kernel image by the command kernel and then run the command boot. You have to define a kernel file and usually an initrd file and the kernel command line, too, before you can run the boot command (see the Grub documentation). How do I load a kernel first?Ĭhange /dev/sda2 with your root partition, change gpt2 with msdos if you don't have a GUID partition table. Rebooting without pressing F12 always reboots in command line mode. Using this technique, it always loads the menu. What works is to reboot using Ctrl+Alt+Del, then pressing F12 repeatedly until the normal GRUB menu appears. There is probably a command that I can type to boot from that prompt, but I don't know it. The reason many installers will ask you if you want to install grub is because you might already have grub installed (usually because you have another linux distro installed and you're going to dual- boot).

Warning: the default settings of the Advanced Options are the recommended ones. When the removal is finished, reboot and check that your system has been removed. Launch OS-Uninstaller, choose the system to remove, then click the "Apply" button. Then launch OS-Uninstaller from the bottom-left menu. A software (Boot-Repair) will be launched automatically, close it. Then install OS-Uninstaller in it, either via PPA for Ubuntu/Mint, or DEBs for Debian.
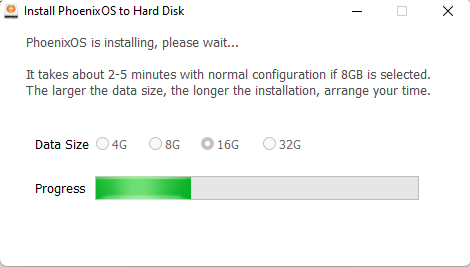
Recommended: boot on a Debian (or derivatives: Ubuntu, Linux Mint.) disk, either normal session, or live-CD, or live-USB.GET OS-UNINSTALLER: whatever the systems installed on your disk, choose one of the 3 methods below:
Remark: if you want to uninstall Wubi (Ubuntu installed inside Windows), please follow this guide. Can remove any Linux (Debian, Ubuntu, Mint, Fedora, OpenSuse, ArchLinux.).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
